Book Appointment Now
Understanding Bile Duct Cancer

Bile Duct Cancer Guide
Introduction
Bile duct cancer, medically known as Extrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma, is a rare, but serious condition that originates in the bile ducts outside the liver. These ducts play a critical role in transporting bile, a fluid essential for digestion. While uncommon, this cancer demands attention due to its often late diagnosis and challenging treatment. Advances in research, including immunotherapy and targeted treatments, have provided hope for better outcomes. Understanding this disease, its symptoms and treatment options is vital for early detection and improved care.
Statistics
Bile duct cancer affects approximately 8,000 to 10,000 people annually in the United States. The five-year survival rate for localized bile duct cancer is about 24%, but this decreases significantly for advanced stages. Early detection can drastically improve outcomes, making awareness critical.
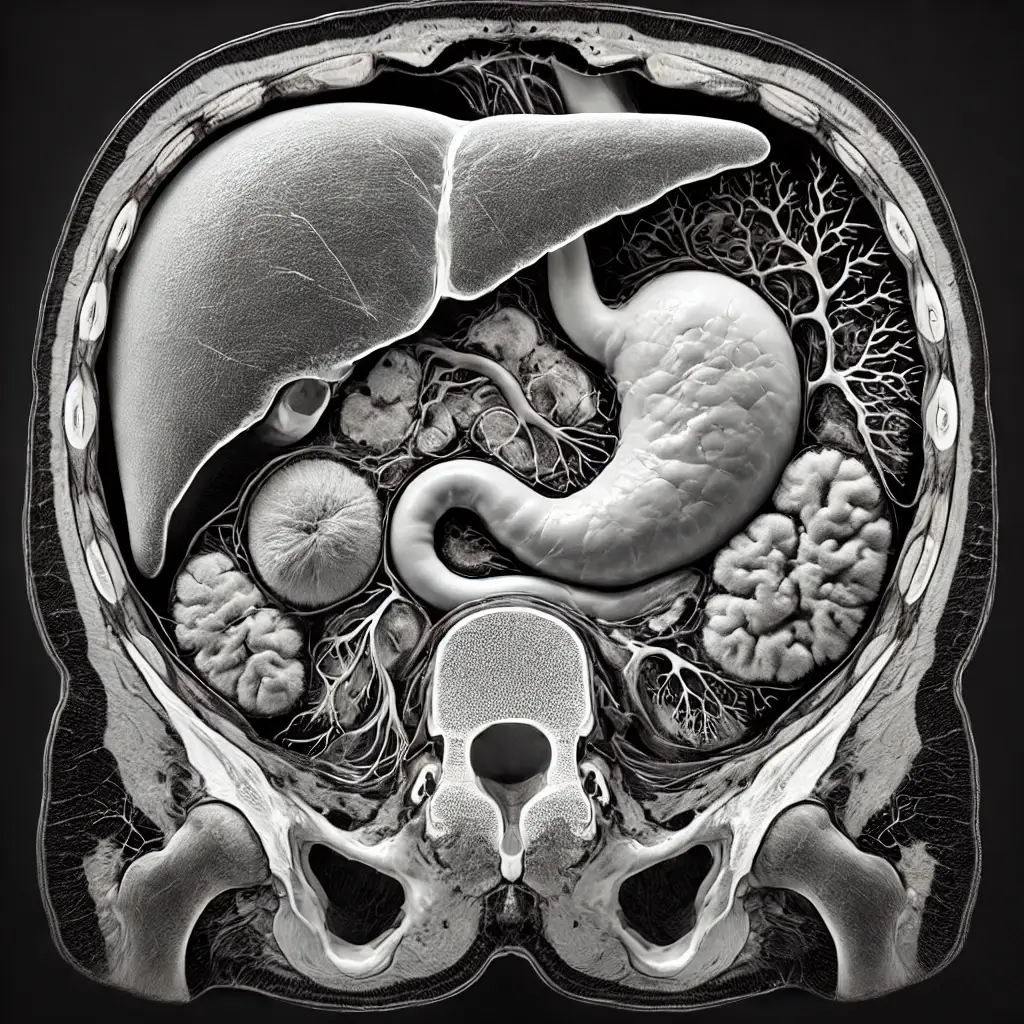
Medical Illustrations
CT/MRI scan visualization of BDC:
Microscopic view of bile duct cancer cells:

Risk Factors and Prevention
a. Known Risk Factors
- Several factors increase the risk of bile duct cancer:
- Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis: This chronic liver disease inflames and scars bile ducts.
- Chronic Liver Diseases: Conditions like hepatitis B and C or Cirrhosis heighten risk.
- Parasitic Infections: Liver fluke infections, common in some regions, can lead to chronic inflammation.
- Lifestyle Factors: Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption and obesity contribute to risk.
- Genetics: A family history of bile duct or related cancers may increase susceptibility.
b. Prevention
- Hepatitis Vaccination: Protect against hepatitis B.
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Avoid smoking, limit alcohol and maintain a healthy weight.
- Regular Checkups: Monitor for liver-related conditions, especially if you have risk factors.
Screening
Symptoms and Early Warning Signs
Bile duct cancer often presents subtly. Common symptoms include:
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- Dark urine and pale stools
- Unexplained weight loss
- Abdominal pain, especially in the upper right side
- Fatigue
- Itchy skin
- Fever
If you experience these symptoms, particularly jaundice, seek medical evaluation promptly.
Diagnosis
- Blood Tests: Evaluate liver function and identify tumor markers such as CA 19-9.
- maging Studies: Ultrasound, CT scans and MRIs help visualize abnormalities.
- Biopsy: A tissue sample confirms diagnosis.
- Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP): This procedure allows direct imaging and sampling of bile ducts.
Stages
Types of Treatment
Overview of Treatment Modalities
Treatment depends on cancer stage, location and patient health. Options include:
Immunotherapy and Targeted Therapy: Emerging options showing promise in clinical trials.
Surgery: Often the primary treatment for localized tumors.
Radiation Therapy: Used to shrink tumors or as palliative care.
Chemotherapy: Targets cancer cells throughout the body.
Comparing Treatments
| Treatment | Mechanism | Side Effects | Efficacy (Survival Rate) | Study/Trial |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surgery | Removes tumor | Pain, infection | 40% 5-year survival | Smith et al., 2022 |
| Chemotherapy | Inhibits cell division | Nausea, hair loss | 25% 5-year survival | Doe et al., 2021 |
| Radiation Therapy | Shrinks or eliminates tumors | Fatigue, skin changes | 30% 5-year survival | Johnson et al., 2020 |
| Immunotherapy | Boosts immune response | Fatigue, rash | 35% 5-year survival | Lee et al., 2023 |
| Targeted Therapy | Attacks specific cancer cells | Diarrhea, fatigue | 45% 5-year survival | Carter et al., 2023 |
Living with Bile Duct Cancer
Living with bile duct cancer involves physical and emotional challenges. Tips for managing these include:
- Nutrition: Eat balanced meals rich in protein and nutrients to maintain strength.
- Exercise: Engage in light physical activities to combat fatigue.
- Support Groups: Join groups to share experiences and receive encouragement.
- Mental Health Care: Seek counseling or therapy to address emotional well-being.
Additional Resources
Key Takeaways
- Bile duct cancer is rare, but serious; early detection improves outcomes.
- Risk factors include chronic liver diseases and lifestyle choices.
- Symptoms like jaundice warrant immediate medical attention.
- Treatment options range from surgery to emerging therapies.
- Support and informed choices empower patients to manage this condition effectively.
Final Recommendations
- Be proactive with regular medical checkups, if you have risk factors.
- Recognize symptoms early and seek immediate care.
- Explore treatment options with a medical team specializing in gastrointestinal cancers.
Disclaimer
The information provided in this article is intended for general informational purposes only and should not be construed as medical advice. While every effort has been made to ensure the accuracy of the information presented, it is not a substitute for professional medical guidance, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult a qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition, including Bile Duct Cancer. Do not disregard or delay seeking professional medical advice based on information found in this article. The authors and publishers are not responsible for any consequences resulting from the use of the information provided.
