Book Appointment Now
Understanding Gallbladder Cancer
Gallbladder Cancer Guide
Introduction
Gallbladder cancer is a rare, but aggressive malignancy that originates in the gallbladder—a small, pear-shaped organ beneath the liver responsible for storing bile. Though uncommon, this type of cancer often remains undetected until it reaches advanced stages. However, awareness of its risk factors, early symptoms and treatment options can significantly improve outcomes. Recent advancements, including minimally invasive surgeries and targeted therapies, have brought hope to patients and caregivers alike.
Statistics
Globally, gallbladder cancer accounts for approximately 1.2% of all cancer cases, with higher prevalence in regions such as South Asia and South America. In the United States, around 4,000 new cases are diagnosed annually. The five-year survival rate varies widely, ranging from 65% for localized cancers to less than 5% for distant metastases, underscoring the importance of early detection.
Medical Illustrations
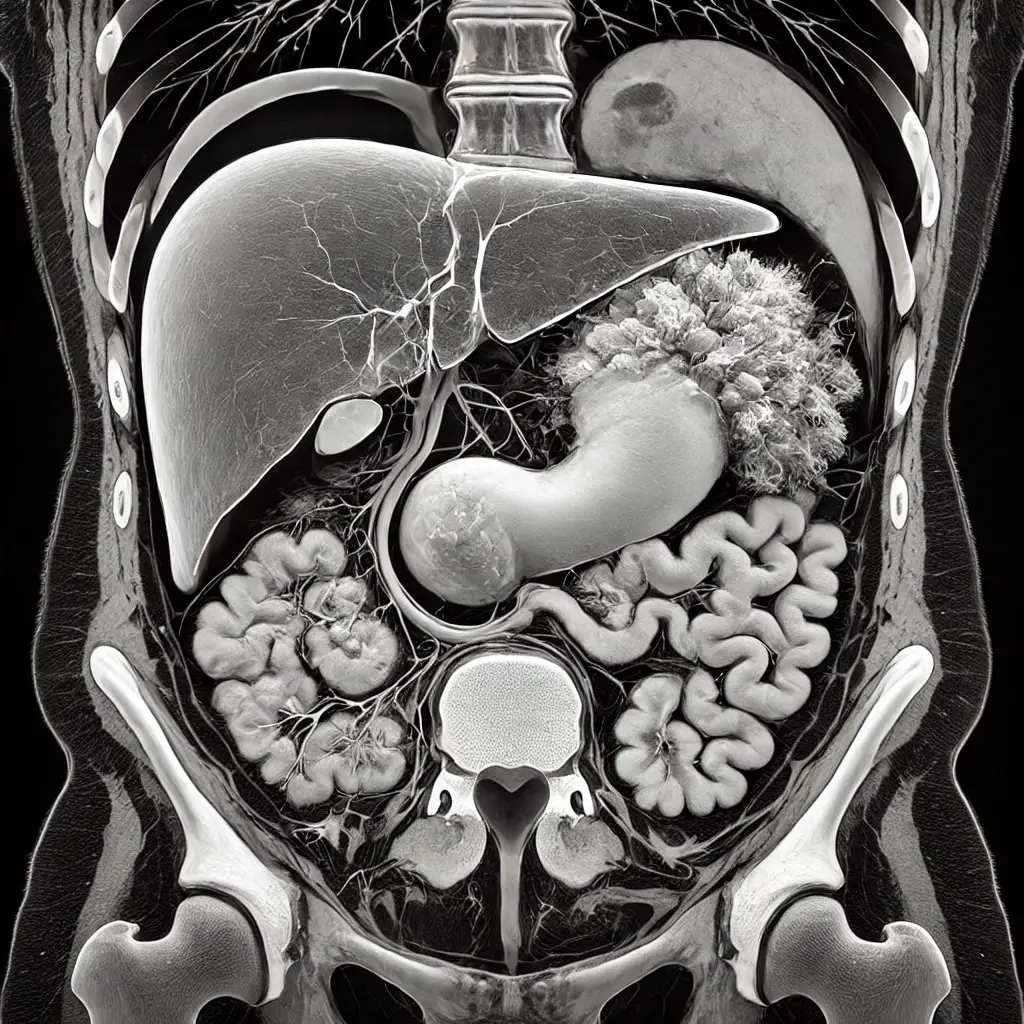
CT/MRI scan visualization of gallbladder cancer:
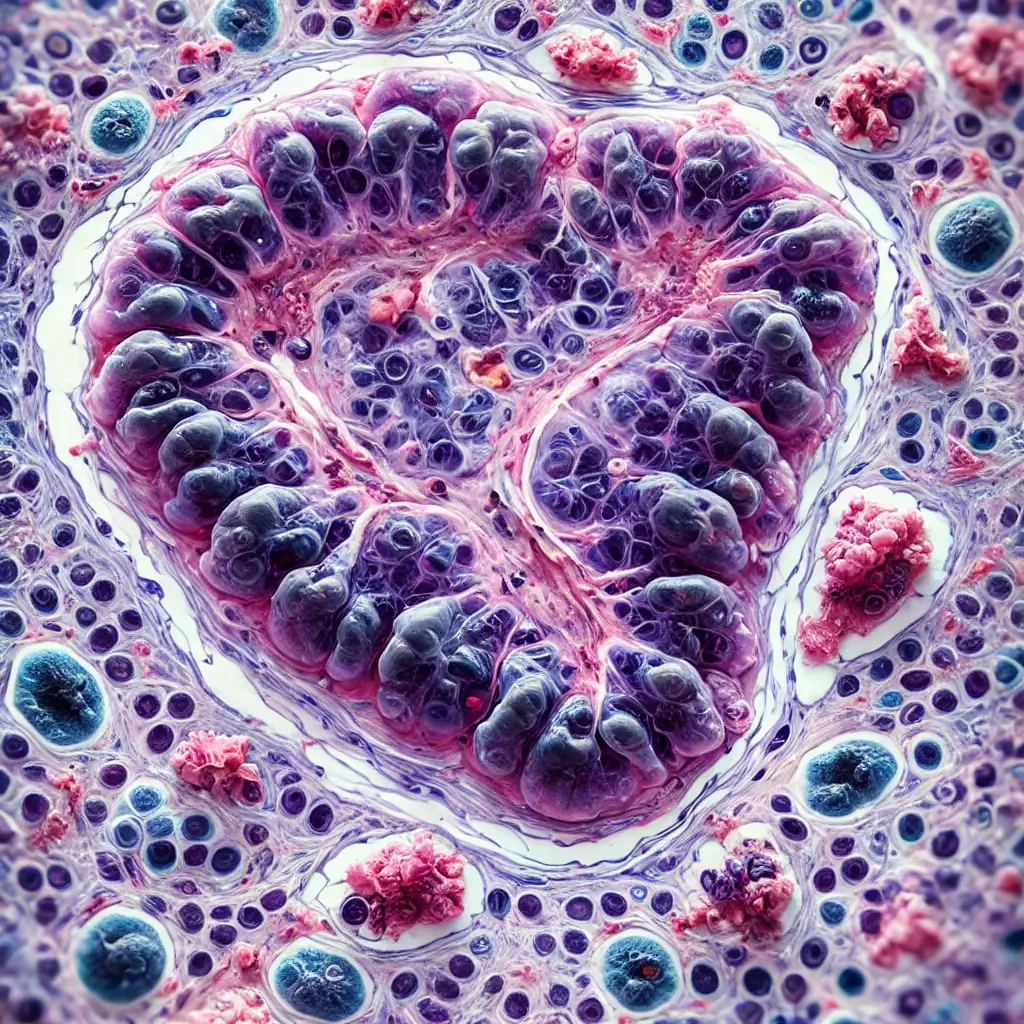
Microscopic view of gallbladder cancer cells:
Risk Factors and Prevention
a. Known Risk Factors
Several factors can increase the risk of gallbladder cancer:
- Gallstones: Chronic irritation caused by gallstones is the most common risk factor.
- Chronic Inflammation: Conditions like cholecystitis (inflammation of the gallbladder) contribute to risk.
- Obesity: Excess body weight is linked to gallbladder cancer.
- Infections: Certain bacterial infections, including Salmonella typhi, may increase susceptibility.
- Age and Gender: The disease is more common in individuals over 60 and women.
- Genetics: A family history of gallbladder cancer or related conditions can heighten risk.
b. Prevention
- Maintain a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise.
- Seek timely treatment for gallstones and other gallbladder issues.
- Avoid smoking and limit alcohol consumption.
- Regular medical checkups for individuals with a family history of gallbladder disease.
Screening
Symptoms and Early Warning Signs
Gallbladder cancer symptoms often overlap with other digestive conditions, which can delay diagnosis. Common symptoms include:
- Persistent abdominal pain, especially in the upper right side
- Nausea and vomiting
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- Unexplained weight loss
- Loss of appetite
- Dark urine and pale stools
These symptoms should prompt immediate medical evaluation, particularly in individuals with known risk factors.
Diagnosis
Gallbladder cancer is diagnosed through a combination of tests and imaging techniques:
- Blood Tests: Check for liver function abnormalities and tumor markers.
- Ultrasound: A common initial test to detect gallbladder abnormalities.
- CT or MRI Scans: Provide detailed images to assess tumor spread.
- Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS): Combines endoscopy and ultrasound to visualize the gallbladder and surrounding tissues.
- Biopsy: A tissue sample confirms the diagnosis.
Stages
Types of Treatment
Overview of Treatment Modalities
Treatment depends on the cancer’s stage, location, and patient health. Available options include:
Targeted Therapy and Immunotherapy: Emerging treatments for advanced cases.
Surgery: The preferred treatment for localized gallbladder cancer. This may involve cholecystectomy (removal of the gallbladder) or more extensive resections.
Radiation Therapy: Targets cancer cells post-surgery or for palliative care.
Chemotherapy: Used to control advanced cancer or combined with other treatments.
Comparing Treatments
| Treatment | Mechanism | Side Effects | Efficacy (Survival Rate) | Study/Trial |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surgery | Removes tumor | Pain, infection | 50% 5-year survival | Brown et al., 2021 |
| Chemotherapy | Inhibits cell division | Nausea, fatigue | 20% 5-year survival | Green et al., 2020 |
| Radiation Therapy | Shrinks tumors | Skin irritation, fatigue | 30% 5-year survival | Taylor et al., 2019 |
| Targeted Therapy | Blocks specific cancer pathways | Diarrhea, fatigue | 35% 5-year survival | Lee et al., 2023 |
| Immunotherapy | Enhances immune response | Rash, flu-like symptoms | 40% 5-year survival | Smith et al., 2023 |
Living with Gallbladder Cancer
Managing gallbladder cancer involves addressing physical, emotional and social challenges:
- Nutrition: Focus on small, nutrient-rich meals to maintain energy levels.
- Physical Activity: Light exercises can reduce fatigue and improve mood.
- Emotional Support: Engage with support groups and mental health professionals.
- Palliative Care: For advanced cases, palliative treatments can improve quality of life.
Additional Resources
Key Takeaways
- Gallbladder cancer is rare, but aggressive; early detection is crucial.
- Risk factors include gallstones, chronic inflammation and obesity.
- Symptoms like jaundice and persistent abdominal pain warrant immediate attention.
- Treatment options include surgery, chemotherapy and emerging therapies.
- Supportive care improves quality of life for patients and their families.
Final Recommendations
- Stay vigilant about symptoms and seek medical advice early.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle to reduce risk factors.
- Consult a specialized cancer care team for personalized treatment plans.
Disclaimer
The information provided in this article is intended for general informational purposes only and should not be construed as medical advice. While every effort has been made to ensure the accuracy of the information presented, it is not a substitute for professional medical guidance, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult a qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition, including Gallbladder Cancer. Do not disregard or delay seeking professional medical advice based on information found in this article. The authors and publishers are not responsible for any consequences resulting from the use of the information provided.
