Book Appointment Now
Understanding Breast Cancer
Breast Cancer Guide
Introduction
Breast cancers is the second most common malignancy in women worldwide, representing a significant public health challenge. The lifetime risk of a woman in the U.S. developing breast cancer is approximately 13%. This article provides an in-depth analysis based on the latest academic research, focusing on breast cancer’s epidemiology, risk factors, diagnostic approaches, treatment modalities, and preventive strategies.
Statistics
Key Statistics:
- Incidence: Breast cancers accounts for around 25% of cancer cases in women.
- Mortality: It remains one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths.
- Survival Rates: The 5-year survival rate for localized breast cancer is approximately 99%. However, survival decreases significantly for advanced stages.
Medical Illustrations
- Breast cancers tumor:
- Axillary lymphadenopathy:
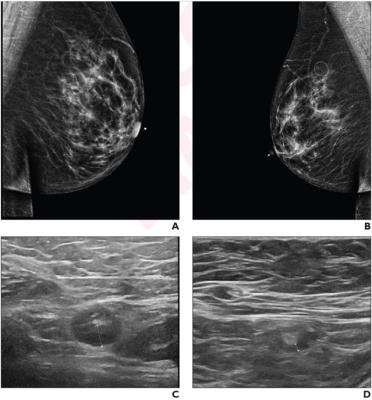
Mammography image:
Risk Factors and Prevention
Known Risk Factors:
Preventive Strategies:
Screening
Current Screening Methods:
Symptoms and Signs
Typical symptoms include:
- Palpable breast masses
- Nipple inversion or discharge.
- Symptoms of metastasis (e.g. bone pain).
Diagnosis
- Physical Examination: Evaluation of breast masses.
- Imaging: Mammography followed by ultrasound or MRI, if necessary.
- Biopsy: Core needle biopsy (CNB) for histological confirmation.
Stages
Types of Treatment
Treatment Modalities:
Following a breast cancer diagnosis, a personalized treatment plan is formulated based on various factors like the cancer stage, grade, and the woman’s overall health. Here’s an overview of the common treatment options for breast cancer:
1. Surgery: Breast-conserving surgery (BCS) or mastectomy.
2. Radiation Therapy: Often used post-surgery to reduce recurrence.
3. Systemic Therapy: Chemotherapy, endocrine therapy, and targeted therapies (e.g., HER2 inhibitors).
Evidence-Based Comparisons
| Treatment | Indications | Mechanism | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tamoxifen | HR+ breast cancer (premenopausal) | Selective estrogen receptor modulator | Reduces risk of recurrence, but with increased VTE risk |
| Anastrozole (Aromatase Inhibitor) | HR+ postmenopausal women | Inhibits estrogen synthesis | Effective in postmenopausal women, lower risk of VTE compared to tamoxifen |
Additional Resources
Disclaimer
This information is intended solely for educational purposes and should not be construed as medical advice. Please consult a healthcare professional for any concerns regarding breast cancer.
