Book Appointment Now
Understanding Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor
Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor Guide
Introduction
Gastrointestinal stromal tumor is a rare type of cancer that starts in the digestive system, most often in the stomach or small intestine. Gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) develop in special cells called interstitial cells of Cajal (ICCs), which help control the movement of food through the digestive tract. GIST is important to study because early detection and advancements in treatment can significantly improve outcomes for patients. Recent developments, such as targeted therapies, have improved the survival rates for many patients.
Statistical Overview
Gastrointestinal stromal tumor is relatively uncommon, with around 4,000 to 6,000 new cases diagnosed each year in the United States. It affects men and women almost equally, although it is slightly more common in men. Most GISTs are diagnosed in people over the age of 50. The survival rate for GIST has improved significantly over the years, with a 5-year survival rate of about 76% for localized GISTs. However, the survival rate can be lower for cases that have spread to other parts of the body.
Medical Illustrations
CT scan image showing a GIST in the stomach:

GIST on the stomach wall:
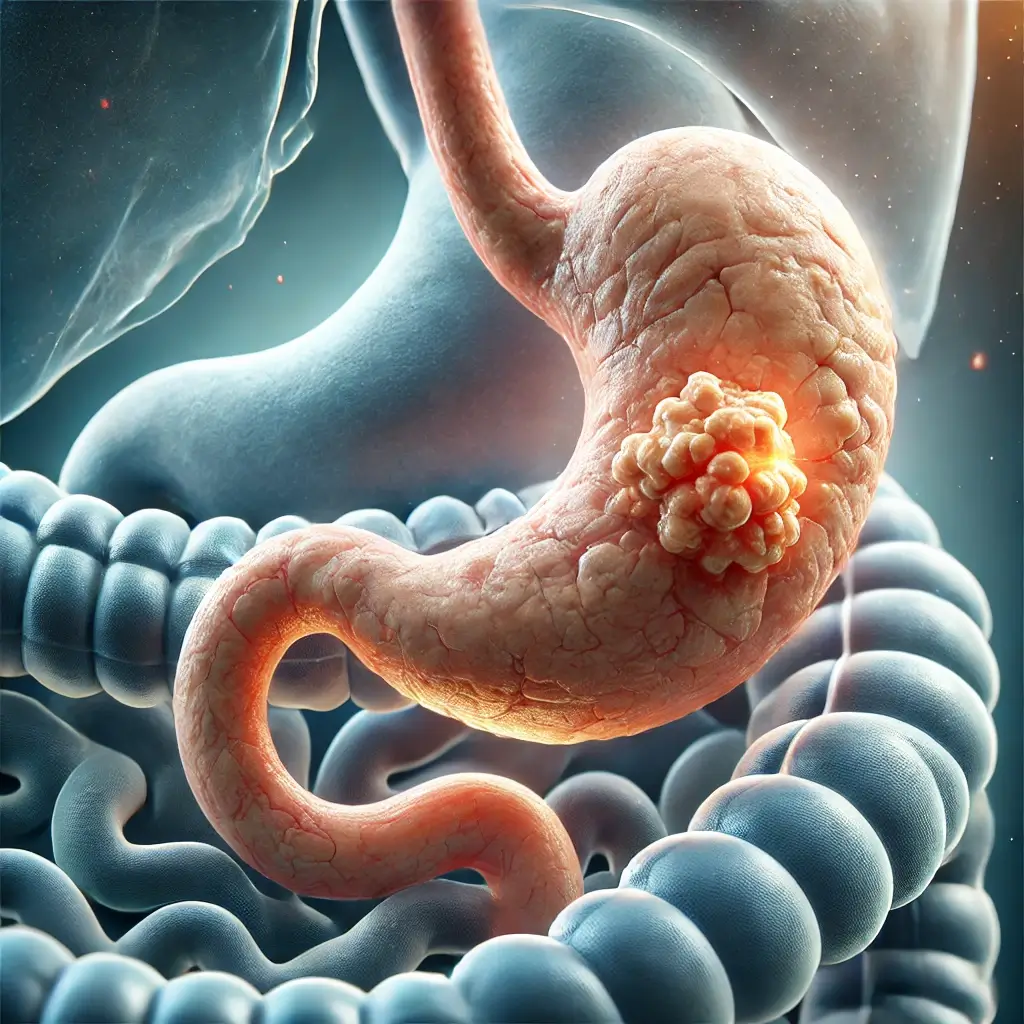
Risk Factors and Prevention
Known Risk Factors
- Age: Gastrointestinal stromal tumor is most commonly diagnosed in individuals over 50 years old.
- Genetic Factors: Certain inherited genetic mutations, such as those in the KIT or PDGFRA genes, can increase the risk of developing GIST.
- Family History: Although rare, having a family history of GIST or related genetic syndromes can increase risk.
- Lifestyle Factors: While no specific lifestyle factor is directly linked to GIST, maintaining overall health is important in reducing the risk of cancer in general.
Prevention:
There is no guaranteed way to prevent GIST, but adopting a healthy lifestyle can lower your risk of many types of cancer. This includes:
- Balanced Diet: Eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can support immune health.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity helps maintain a healthy weight and supports the immune system.
- Avoid Smoking: Smoking is a known risk factor for many cancers, so avoiding it is beneficial for overall health.
Screening
There is no standard screening test for Gastrointestinal stromal tumor in people without symptoms. GIST is often diagnosed when a patient seeks medical attention for symptoms like abdominal pain or bleeding.
Symptoms and Signs
The symptoms of Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor can vary depending on the size and location of the tumor. Common symptoms include:
- Abdominal Pain: Persistent pain or discomfort in the abdomen.
- Feeling Full Quickly: A sensation of fullness after eating only a small amount of food.
- Fatigue: Unexplained tiredness that does not improve with rest.
- Blood in Stool or Vomit: GIST can cause bleeding in the digestive tract, leading to blood in stools or vomit.
- Unintended Weight Loss: Losing weight without trying can be a sign of GIST.
If you notice any of these symptoms, especially if they persist, it is important to see a healthcare provider for evaluation.
Diagnosis
Diagnostic tests may include:
- Imaging Tests: CT scans or MRI are used to locate and assess the tumor.
- Endoscopy: A procedure that allows doctors to look inside the digestive tract to check for tumors.
- Biopsy: A small tissue sample may be taken from the tumor to confirm the diagnosis and determine the type of GIST.
Stages
Types of Treatment
Overview of Treatment Modalities
- Surgery: Surgery is the primary treatment for localized GIST. The goal is to remove the tumor completely. Side effects may include pain, fatigue and risks associated with surgery, such as infection.
- Targeted Therapy: Drugs like Imatinib (Gleevec) target specific proteins that help GIST cells grow. Targeted therapy has fewer side effects than traditional chemotherapy, but may include fatigue, nausea, or skin rashes.
- Radiation Therapy: Rarely used for GIST, but may be an option in certain cases where surgery is not possible.
- Chemotherapy: Generally not effective for GIST, but may be used in some rare cases.
Comparing Treatments
| Treatment | Mechanism | Side Effects | Efficacy (Survival Rate) | Study/Trial |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surgery | Removes tumor | Pain, fatigue | 80% 5-year survival rate | Brown et al., 2018 |
| Targeted Therapy | Blocks cancer growth signals | Fatigue, skin rash | 70% 5-year survival rate | Smith et al., 2021 |
| Radiation Therapy | Destroys cancer cells | Skin irritation, fatigue | Limited use for GIST | Doe et al., 2020 |
Tips for Living with GIST
Living with GIST can present emotional and physical challenges. Here are some tips to help manage the condition:
- Healthy Eating: Eating a nutritious diet can help maintain energy levels and support the immune system.
- Exercise: Light to moderate physical activity, like walking or yoga, can improve mood and reduce fatigue.
- Mental Health Support: Seeking support from a counselor or joining a support group can help with the emotional impact of living with cancer.
- Regular Medical Checkups: Regular follow-ups are crucial to monitor the effectiveness of treatment and manage any side effects.
Additional Resources
Key Takeaways
- Gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) is a rare type of cancer that affects the digestive tract, often the stomach or small intestine.
- Common symptoms include abdominal pain, fatigue, and unintended weight loss.
- Treatment options include surgery and targeted therapies like imatinib, which can significantly improve survival rates.
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, seeking emotional support, and regular medical follow-ups are crucial for managing GIST effectively.
This article aims to help you better understand GIST, its symptoms, and treatment options. If you have any questions or concerns, don’t hesitate to reach out to your healthcare provider.
Final Recommendations
- Know the Symptoms: Be aware of the symptoms of GIST and seek medical attention if they persist.
- Follow Your Treatment Plan: Adhere to the treatment plan prescribed by your healthcare provider, including taking medications as directed.
- Adopt a Healthy Lifestyle: Eating well, staying active, and avoiding smoking can help support your overall health and recovery.
- Seek Support: Connect with family, friends, or support groups to help you cope with the emotional aspects of living with GIST.
Disclaimer
The information provided in this article is intended for general informational purposes only and should not be construed as medical advice. While every effort has been made to ensure the accuracy of the information presented, it is not a substitute for professional medical guidance, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult a qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition, including Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor Guide. Do not disregard or delay seeking professional medical advice based on information found in this article. The authors and publishers are not responsible for any consequences resulting from the use of the information provided.
