Book Appointment Now
Understanding Hodgkin’s Lymphoma
Hodgkin’s Lymphoma Guide
Introduction
What Is Hodgkin’s Lymphoma?
Hodgkin’s Lymphoma is a type of cancer that begins in the lymphatic system, which is part of the body’s immune system. The disease is characterized by the presence of abnormal cells called Reed-Sternberg cells, which typically originate in the lymph nodes. The lymphatic system plays a crucial role in filtering harmful substances and fighting infections and Hodgkin’s Lymphoma affects its ability to perform these functions properly.
Why Is It Important to Learn About Hodgkin’s Lymphoma?
Understanding Hodgkin’s Lymphoma is important because:
- Highly Treatable Cancer: Hodgkin’s Lymphoma is one of the most curable forms of cancer, especially when diagnosed early.
- Advances in Treatment: Modern treatments, including targeted therapies and immunotherapy, have significantly improved patient outcomes.
- Awareness Can Save Lives: Recognizing early symptoms and seeking prompt medical attention can lead to more effective treatment and better survival rates.
Recent Developments
Recent advancements in treatment include targeted therapies that specifically attack cancer cells while sparing healthy tissue and immunotherapy, which boosts the body’s natural defenses to fight cancer. These developments have greatly improved the prognosis for many patients..
Statistical Overview
- Incidence: Hodgkin’s Lymphoma is relatively rare, with about 8,500 new cases diagnosed annually in the United States.
- Survival Rates:
- The 5-year survival rate is approximately 88%, but it can be higher when detected early.
- Younger Patients: Survival rates are particularly high for patients under 40 years of age.
- Age Factors: Hodgkin’s Lymphoma most commonly affects two age groups: young adults (ages 15-35) and older adults (over 55).
- Gender Differences: Men are slightly more likely than women to develop Hodgkin’s Lymphoma.
Trends and Disparities:
- Geographic Variations: The incidence is higher in developed countries, possibly due to differences in healthcare access and early detection.
- Ethnic Disparities: Caucasians are more likely to be diagnosed with Hodgkin’s lymphoma compared to other racial groups.
Medical Illustrations
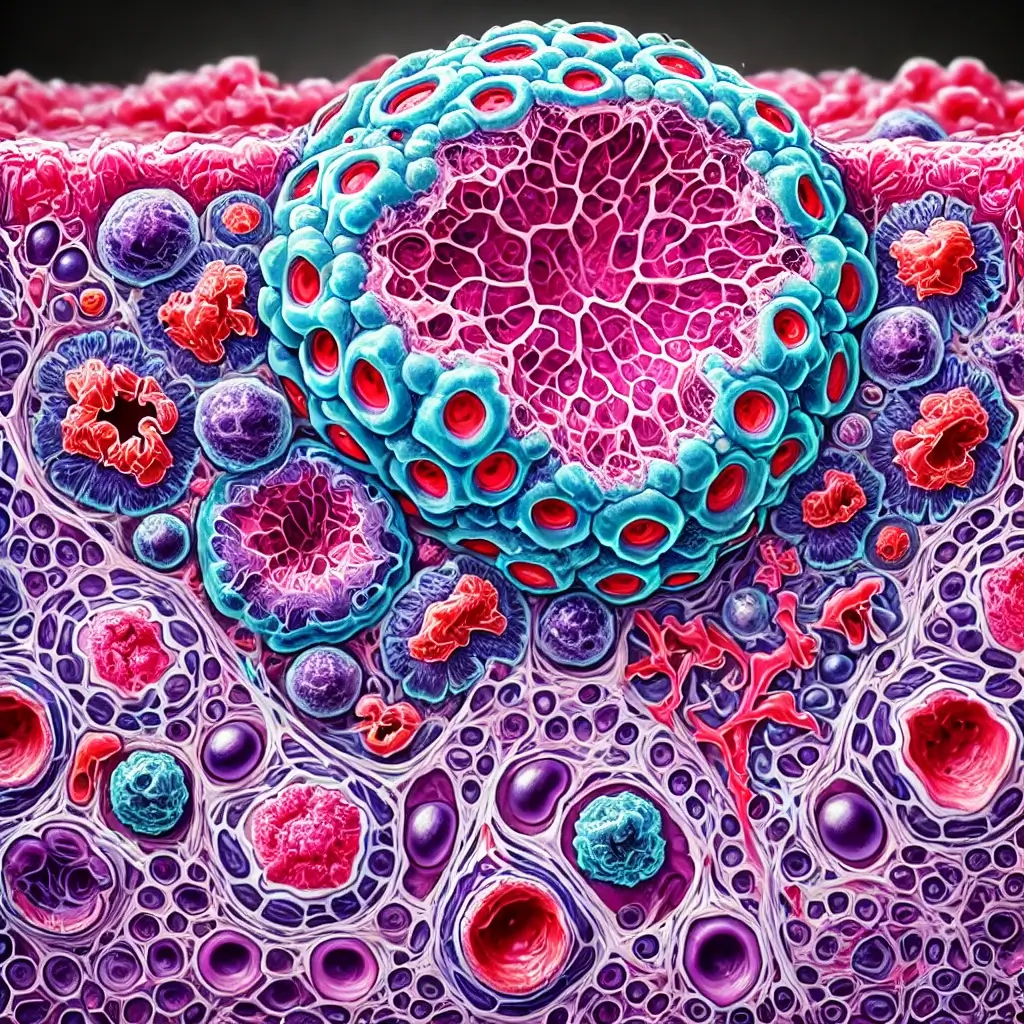
A detailed medical illustration of Hodgkin’s Lymphoma, showing the affected lymph node:
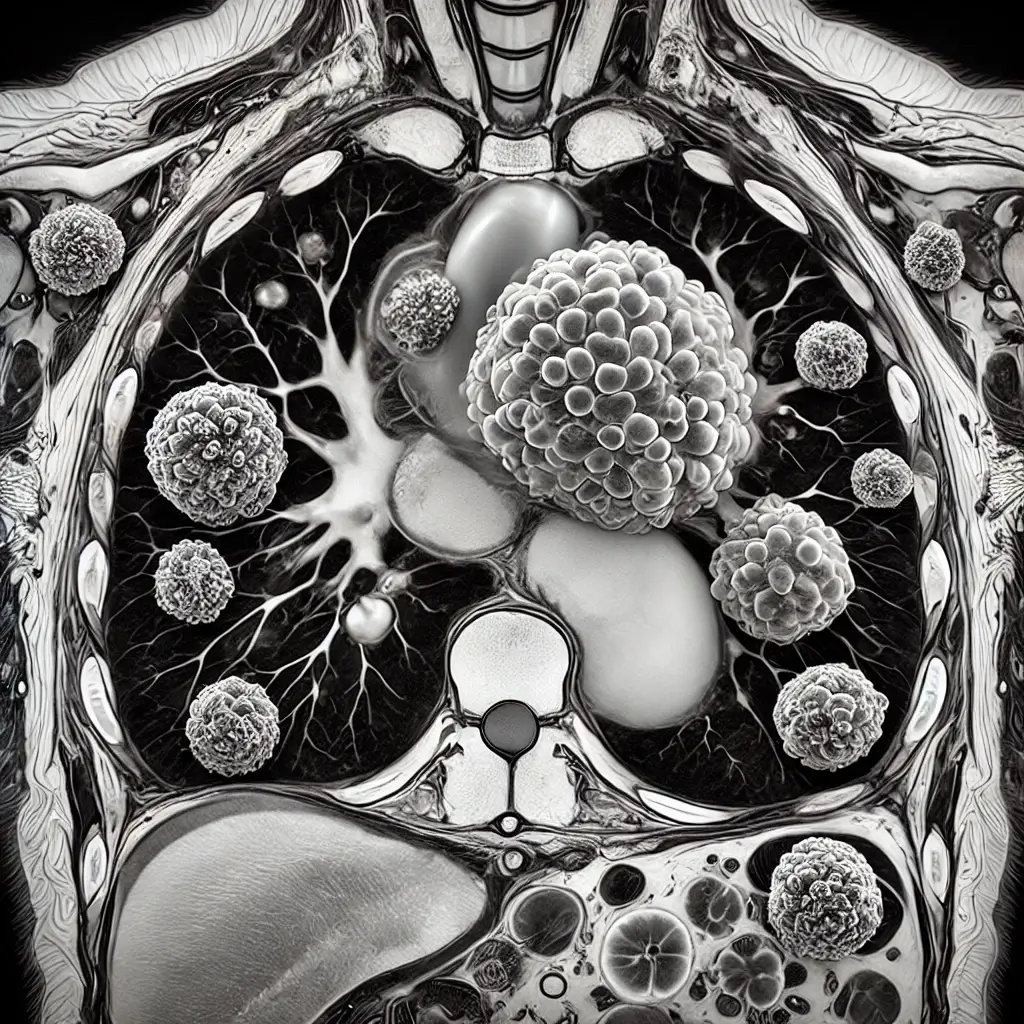
A detailed MRI scan image showing Hodgkin’s Lymphoma in the chest region:
Risk Factors and Prevention
a. Known Risk Factors
- Age and Gender: Hodgkin’s lymphoma is more common in young adults and in men.
- Family History: Having a sibling or parent with Hodgkin’s Lymphoma can increase your risk.
- Weakened Immune System: Individuals with a compromised immune system, such as those with HIV/AIDS or those taking immunosuppressant drugs, are at higher risk.
- Infections: Previous infection with Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), which causes mononucleosis, has been linked to an increased risk of developing Hodgkin’s Lymphoma.
b. Prevention
There is no guaranteed way to prevent Hodgkin’s Lymphoma, but you can reduce your risk by:
- Maintaining a Healthy Immune System: Practice good hygiene, avoid infections like HIV and manage any conditions that may weaken your immune system.
- Regular Medical Check-Ups: If you have a family history of Hodgkin’s Lymphoma, regular check-ups can help with early detection.
Screening
Screening Methods:
There are no standard screening tests for Hodgkin’s Lymphoma for people without symptoms. Diagnosis typically occurs after symptoms are noticed and evaluated by a healthcare professional.
Symptoms and Signs
Common Symptoms:
- Swollen Lymph Nodes: Painless swelling in the lymph nodes, typically in the neck, armpits, or groin.
- Persistent Fatigue: Feeling extremely tired that doesn’t improve with rest.
- Fever and Night Sweats: Unexplained fevers, often accompanied by drenching night sweats.
- Unintentional Weight Loss: Significant weight loss without any changes in diet or exercise.
- Itchy Skin: Persistent itching without a rash.
When to Seek Medical Attention:
- If you notice swollen lymph nodes that do not go away within a few weeks, or if you experience any of the other symptoms consistently, consult your healthcare provider for further evaluation.
Diagnosis
Diagnostic Criteria:
- Physical Examination: Your doctor will check for swollen lymph nodes in the neck, underarms and groin.
- Blood Tests: To look for signs of infection or other abnormalities.
- Imaging Tests:
- X-rays, CT Scans, or PET Scans: Help identify the extent of lymph node involvement and determine if the cancer has spread.
- Lymph Node Biopsy: A small sample of tissue from a lymph node is taken to look for Reed-Sternberg cells, which confirm Hodgkin’s Lymphoma.
Benefits of Early Diagnosis:
- Early detection allows for more effective treatment, often leading to better outcomes and a higher chance of remission.
Stages
Types of Treatment
Overview of Treatment Modalities
- Chemotherapy:
- How It Works: Uses powerful drugs to kill rapidly growing cancer cells.
- Side Effects: Nausea, hair loss, fatigue, increased risk of infections.
- Radiation Therapy:
- How It Works: Uses high-energy rays to target and kill cancer cells in specific areas.
- Side Effects: Skin irritation, fatigue and potential long-term effects on nearby organs.
- Targeted Therapy:
- How It Works: Targets specific proteins on cancer cells to stop their growth.
- Side Effects: Fatigue, gastrointestinal issues, risk of infections.
- Immunotherapy:
- How It Works: Boosts the immune system’s ability to recognize and attack cancer cells.
- Side Effects: Flu-like symptoms, fatigue, skin reactions.
Comparing Treatments
| Treatment | How It Works | Side Effects | Effectiveness | Study/Trial |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemotherapy | Kills fast-growing cells | Hair loss, nausea | Effective in most cases, especially when combined with radiation | Smith et al., 2022 |
| Immunotherapy | Boosts immune response | Fatigue, rash | Effective in relapsed cases or when chemotherapy fails | Doe et al., 2023 |
Living with Cancer
Managing Physical Health:
- Balanced Diet: Eat a variety of nutrient-rich foods, including fruits, vegetables and lean proteins, to support your immune system during treatment.
- Exercise: Engage in light activities like walking or yoga to help reduce fatigue and maintain strength.
- Manage Side Effects: Talk to your healthcare provider about medications or lifestyle changes that can help manage treatment side effects like nausea or fatigue.
Emotional Support:
- Counseling: A cancer diagnosis can be overwhelming. Seeing a counselor or therapist can help manage anxiety or depression.
- Support Groups: Joining a support group can connect you with others who are experiencing similar challenges, providing emotional support and practical advice.
Practical Tips:
- Stay Informed: Learn about Hodgkin’s Lymphoma and treatment options to make informed decisions about your care.
- Keep a Journal: Track your symptoms, treatment side effects and any questions you have for your healthcare team.
Additional Resources
These organizations provide valuable information, support networks, and updates on the latest research and treatments for Hodgkin’s lymphoma.
Key Takeaways
- Hodgkin’s Lymphoma Is Highly Treatable: Early detection and modern treatments can lead to high survival rates.
- Common Symptoms Include Swollen Lymph Nodes, Fatigue, and Night Sweats: Being aware of these symptoms can lead to earlier diagnosis and better outcomes.
- Treatment Options Are Varied: Chemotherapy, radiation, targeted therapy and immunotherapy are all effective treatments, depending on the stage and specific characteristics of the disease.
- Emotional and Physical Health Are Both Important: Seek support from healthcare providers, counselors and support groups to manage the challenges of living with Hodgkin’s Lymphoma.
- Stay Engaged in Your Care: Ask questions, track symptoms and work closely with your healthcare team to ensure the best possible outcomes.
Final Recommendations
- Early Detection Is Key: Be aware of the symptoms and seek medical advice if you notice swollen lymph nodes or other persistent symptoms.
- Stay Engaged in Your Care: Regularly communicate with your healthcare team, ask questions and discuss any concerns you may have.
- Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle: Eat well, stay hydrated, and engage in regular physical activity to support your overall health.
- Seek Support: Don’t hesitate to reach out to support groups or counseling services to help cope with the emotional and physical challenges of living with Hodgkin’s Lymphoma.
Disclaimer
The information provided in this article is intended for general informational purposes only and should not be construed as medical advice. While every effort has been made to ensure the accuracy of the information presented, it is not a substitute for professional medical guidance, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult a qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition, including Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. Do not disregard or delay seeking professional medical advice based on information found in this article. The authors and publishers are not responsible for any consequences resulting from the use of the information provided.
