Book Appointment Now
CT Scanners in Oncology: Revolutionizing Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment
Introduction
Cancer remains one of the leading causes of morbidity and mortality worldwide. Early detection and accurate diagnosis are crucial for effective treatment and improved patient outcomes. Computed Tomography (CT) scanners have become an indispensable tool in oncology, providing detailed images that aid in the detection, diagnosis, staging, and monitoring of cancer. In recent years, advancements such as low-dose imaging and artificial intelligence integration have further enhanced their role in cancer care.
Detailed Description
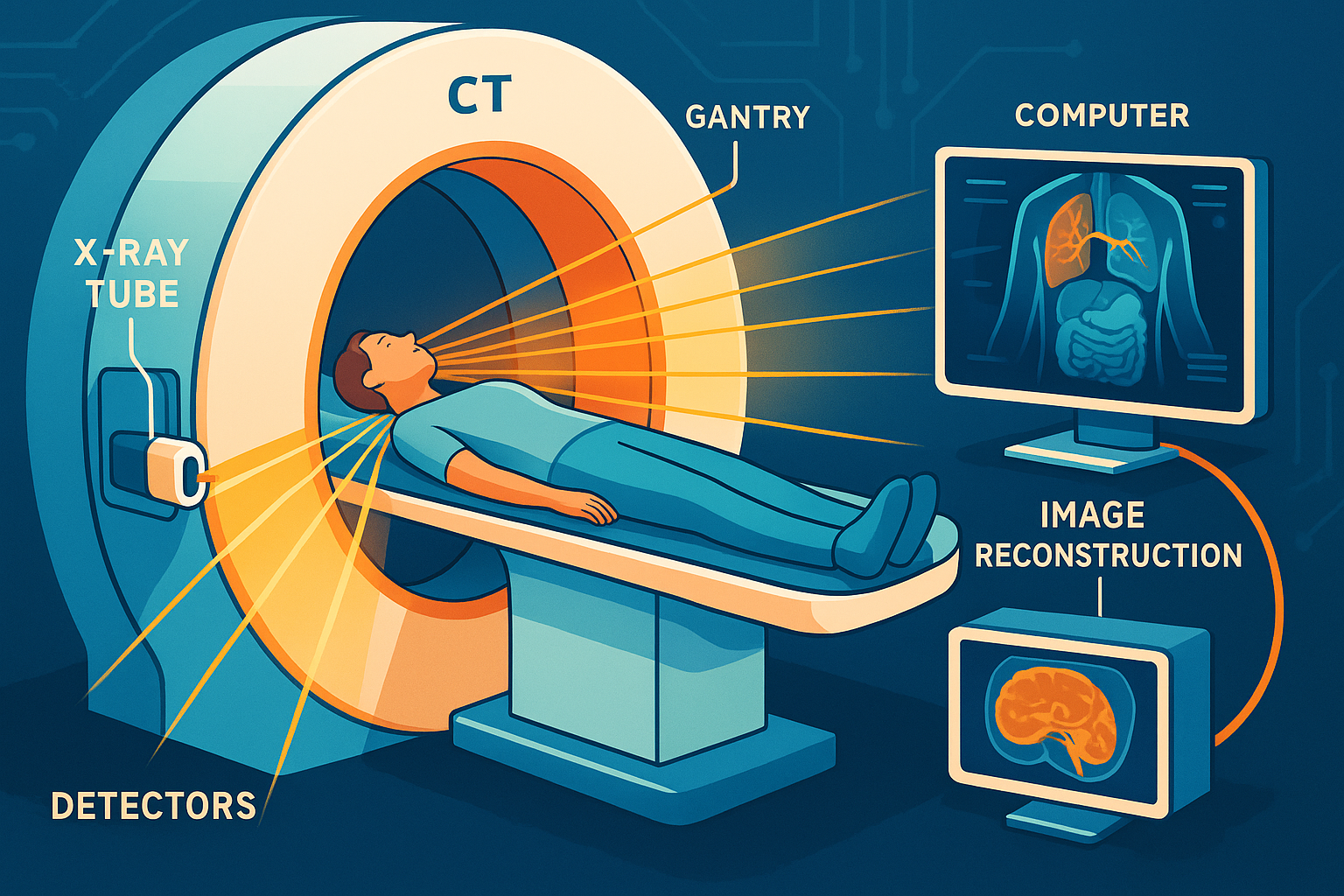
A CT scanner is a sophisticated medical imaging device that uses X-rays and computer processing to create cross-sectional images of the body’s internal structures. Unlike traditional X-rays that provide flat, two-dimensional images, CT scans offer detailed, three-dimensional views of organs, bones, and tissues.
Key Components:
- X-ray Tube: Emits X-rays that penetrate the body.
- Detectors: Capture X-rays after they pass through the body.
- Gantry: The circular frame that houses the X-ray tube and detectors, rotating around the patient.
- Computer System: Processes data to construct images.
Patient Table (Couch): Moves the patient through the gantry during the scan.
How It Works:
In simple terms, the CT scanner’s X-ray tube rotates around the patient, emitting narrow beams of X-rays from various angles. As these beams pass through the body, they are absorbed differently by various tissues. Detectors on the opposite side capture the X-rays that make it through. The computer then reconstructs these signals into cross-sectional images—or “slices”—of the body. When stacked together, these slices form a comprehensive, three-dimensional representation of the internal anatomy.

Applications in Oncology
CT scanners are vital in multiple facets of cancer care:
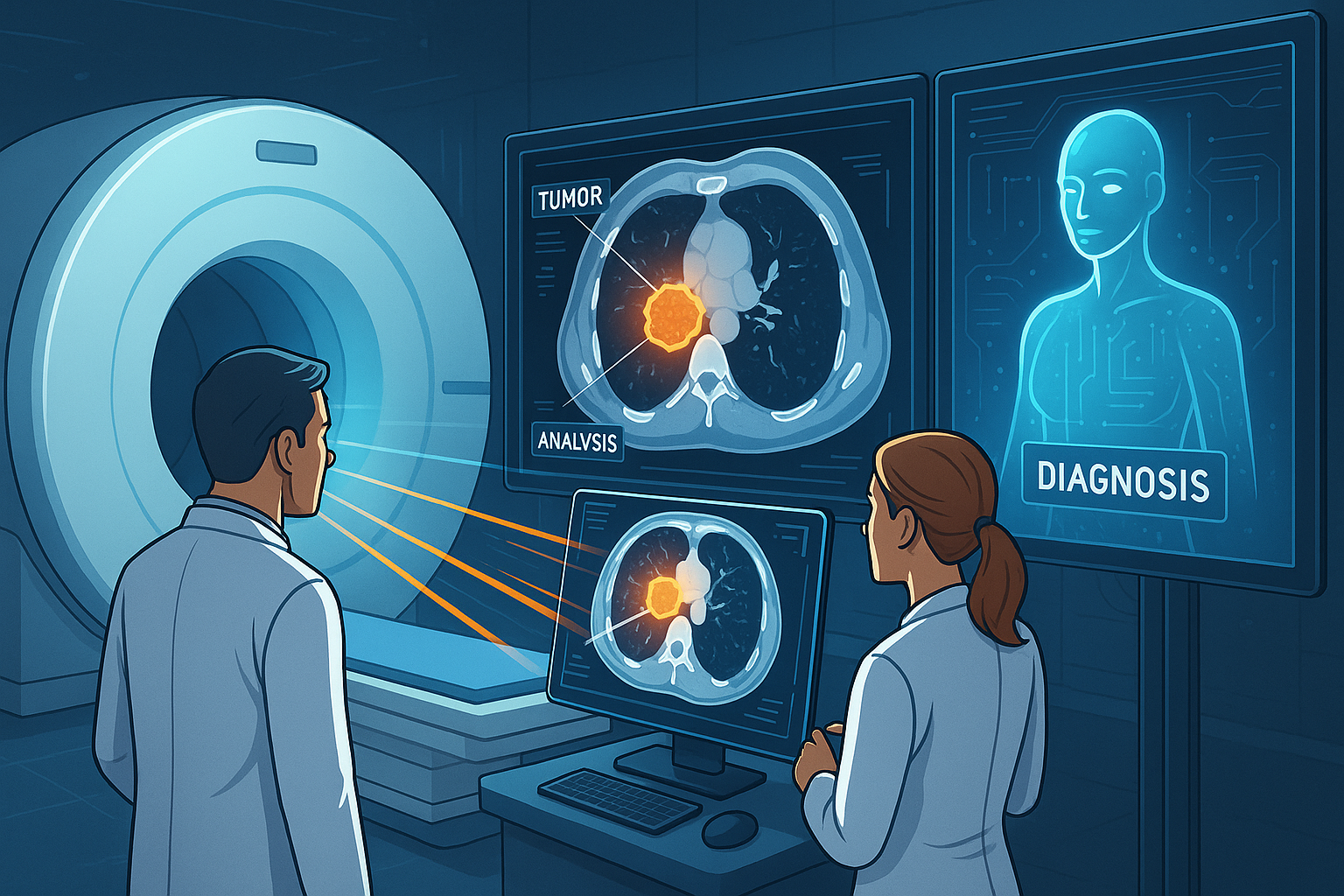
1. Detection and Diagnosis
- Identifying Tumors: CT scans can reveal the presence of tumors in organs like the lungs, liver, kidneys, and brain.
- Characterizing Lesions: Helps differentiate between benign and malignant masses.
- Guided Biopsies: Assists doctors in precisely locating and sampling suspicious tissues.
Scenario: A patient experiences unexplained headaches. A CT scan of the head reveals a small mass in the brain. Early detection allows for prompt intervention, significantly improving the patient’s prognosis.
2. Staging of Cancer
- Assessing Spread: Determines if cancer has metastasized to lymph nodes or other organs.
- Treatment Planning: Helps oncologists decide on surgery, chemotherapy, radiation or a combination.
3. Treatment Guidance
- Radiation Therapy Planning: CT images help define the exact location and size of tumors for targeted radiation.
- Surgical Planning: Surgeons use CT scans to navigate complex anatomical areas safely.
4. Monitoring Progress
- Evaluating Treatment Efficacy: Regular CT scans assess how tumors respond to therapy.
- Detecting Recurrence: Post-treatment scans monitor for any signs of cancer returning.
5. Interventional Procedures
- Minimally Invasive Treatments: Guides procedures like ablations, where tumors are destroyed using heat or cold without open surgery.
Advantages and Limitations
Advantages:
- High Resolution: Provides detailed images of bones, organs and soft tissues.
- Speed: Quick scanning reduces the time patients need to hold still.
- Non-Invasive: No surgical incisions are required.
- Versatility: Can image virtually any part of the body.
- Guidance Capability: Assists in precise placement during biopsies and treatments.
Limitations:
- Not Always Definitive: May require additional tests for a complete diagnosis.malignant lesions.
- Radiation Exposure: Uses ionizing radiation, which carries a risk, especially with repeated exposure.
- Cost: Can be expensive, potentially limiting accessibility.
- Contrast Allergies: Some patients may react to contrast agents used to enhance images.
Recent Developments and Innovations
1. Low-Dose CT Scanning
- Reduced Radiation: Newer machines use advanced algorithms to minimize radiation exposure without compromising image quality.
- Screening Programs: Low-dose CT scans are now used for lung cancer screening in high-risk populations.
2. Dual-Energy CT
- Enhanced Detail: Captures images at two different energy levels, improving tissue characterization and lesion detection.
3. Artificial Intelligence Integration
- Improved Accuracy: AI algorithms assist in detecting abnormalities and measuring tumor size.
- Workflow Efficiency: Automates routine tasks, allowing radiologists to focus on complex cases.
4. Faster Scanning Times
- Patient Comfort: Shorter scans reduce discomfort and the need for sedation in some patients.
5. Portable and Cone-Beam CT Scanners
- Accessibility: Portable units bring imaging to patients who cannot be easily moved, such as those in intensive care.
6. Functional Imaging
- Perfusion CT: Measures blood flow to tumors, aiding in assessing aggressiveness and treatment response.
Ongoing research aims to further enhance image resolution, reduce radiation doses and expand the diagnostic capabilities of CT technology.
Safety and Patient Comfort
Safety Features:
- Dose Optimization: Techniques like automatic exposure control adjust the radiation dose based on patient size and the area scanned.
- Regular Calibration: Ensures equipment operates safely and effectively.
- Compliance Standards: Adheres to regulations set by organizations like the FDA and International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC).
Patient Comfort Considerations:
- Non-Invasive Procedure: Generally painless with minimal discomfort.
- Open Design Scanners: Reduce feelings of claustrophobia with wider openings.
- Communication: Technologists can communicate with patients during the scan for reassurance.
- Comfortable Environment: Efforts are made to create a soothing atmosphere in scanning rooms.
Addressing Patient Concerns:
- Preparation Guidance: Clear instructions are provided to ensure patients are comfortable and informed.
- Radiation Risks: The minimal risk is outweighed by the diagnostic benefits and efforts are made to use the lowest effective dose.
- Contrast Reactions: Patients are screened for allergies; alternative agents or pre-medication can be used if necessary.
Conclusion
CT scanners have transformed cancer care by providing rapid, detailed images essential for diagnosis, staging and treatment planning. Their ability to visualize internal structures with precision makes them a critical tool in oncology. Advancements like low-dose scanning and AI integration continue to enhance their effectiveness and safety.
Looking forward, CT technology is poised to become even more integral to cancer care. Future developments may include further dose reductions, enhanced imaging capabilities and greater use of AI for image interpretation. These innovations promise to improve diagnostic accuracy and personalize treatment, offering hope for better patient outcomes.
References
- American Cancer Society. (2023). Imaging (Radiology) Tests for Cancer.
- Radiological Society of North America. (2023). Computed Tomography (CT).
- National Cancer Institute. (2023). Cancer Imaging Technology.
For more information on cancer care and advancements in oncology equipment, visit CancersHub.com.
Feel free to explore more about CT scanners and other medical equipment that are revolutionizing cancer care. Understanding these tools can provide reassurance and empower patients and their families during their cancer journey.



